Overview
- The accounts receivable turnover ratio measures how efficiently a business collects payments from customers and manages credit sales.
- A higher turnover ratio indicates timely collection and strong cash flow management, while a lower ratio may signal issues in credit policies or payment delays.
- The ratio is calculated by dividing net credit sales by the average accounts receivable during a specific period.
- Regularly tracking this metric helps businesses identify trends, improve credit terms, and optimize working capital.
- JMAccountingServices guides businesses in analyzing and improving their accounts receivable turnover to strengthen financial performance and liquidity.
How is Accounts Receivable Turnover Calculated
The Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio is a key metric used to measure how efficiently a business collects its outstanding credit sales within a specific period. This article explores what the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio means, how it is calculated, and why it plays a vital role in evaluating a company’s financial health. Understanding this ratio helps businesses, such as startups and retail companies, determine how quickly they convert their receivables into cash and assess the effectiveness of their credit and collection policies. The analysis is based on credible sources, including reports from the CPA Journal and studies from accounting institutions that emphasize the importance of turnover ratios in business performance evaluation.
What Is Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
The Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio is a financial metric that measures how efficiently a company collects payments from its customers during a given accounting period. This ratio indicates the number of times receivables are converted into cash and renewed over a specific timeframe. According to research from the Journal of Accountancy, a higher turnover ratio signifies efficient credit management and strong collection practices, while a lower ratio indicates potential delays in cash inflows.
For example, many companies, such as software firms and e-commerce businesses, extend credit to customers, which temporarily ties up funds. By tracking the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio, these businesses can assess whether their credit policies are promoting liquidity or causing cash flow issues. A ratio of 10, for instance, means that receivables are collected ten times a year, suggesting quick customer payments and efficient management of working capital.
The ratio’s interpretation depends on industry standards. According to a 2024 QuickBooks survey, industries like retail and hospitality tend to have faster turnover rates compared to construction and manufacturing. Therefore, companies should compare their ratio against industry benchmarks to determine financial efficiency.
How Is Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio Calculated?
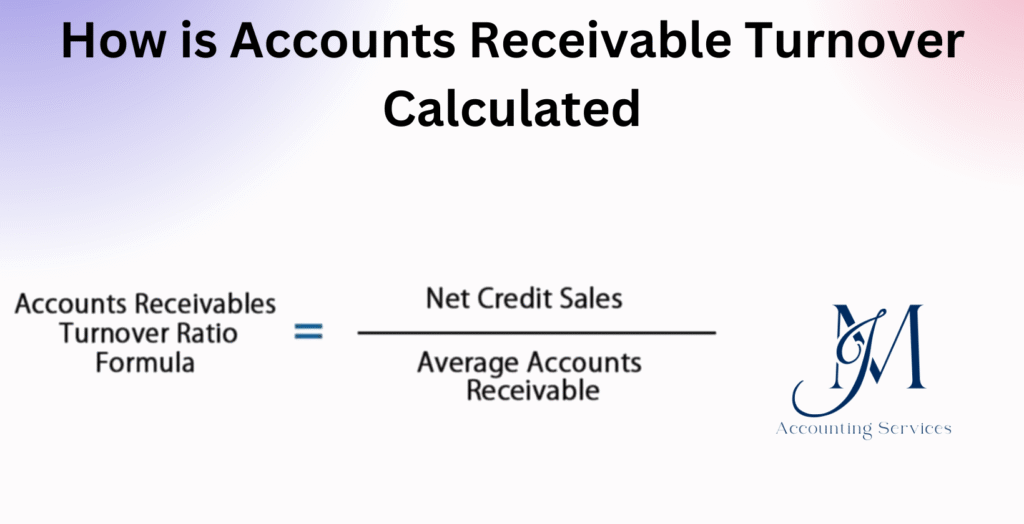
The Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio is calculated by dividing the company’s net credit sales by its average accounts receivable during a specific period. The formula is:
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales ÷ Average Accounts Receivable
For instance, assume a company records $500,000 in net credit sales for the year and maintains an average accounts receivable of $50,000. The ratio would be 10 ($500,000 ÷ $50,000), meaning the business collects its receivables approximately ten times annually. This data reveals that, on average, customers pay their invoices every 36 days (365 ÷ 10).
When calculating, businesses must use net credit sales (total credit sales minus returns and allowances) instead of total sales, since cash sales do not create receivables. The average accounts receivable is obtained by adding the beginning and ending balances of receivables and dividing by two.
Industry experts such as the CPA Practice Advisor recommend calculating this ratio quarterly or annually to identify trends in credit management efficiency. For example, a declining ratio over several periods may indicate worsening customer payment behavior or overly lenient credit policies. Conversely, an increasing ratio reflects effective collection strategies and strong customer payment discipline.
Companies aiming to improve their ratio can shorten credit terms, use invoice reminders, and offer early payment discounts. Skilled professionals can be found through JMAccountingServices, where businesses can hire experienced accounting experts to evaluate and optimize their receivable cycles.
What Is the Formula for Average Accounts Receivable in Turnover Calculations?
The formula for Average Accounts Receivable in turnover calculations is obtained by adding the beginning accounts receivable and the ending accounts receivable, then dividing the sum by two. The formula is:
Average Accounts Receivable = (Beginning Accounts Receivable + Ending Accounts Receivable) ÷ 2
This formula helps determine the typical balance of receivables held during an accounting period, allowing businesses to measure how efficiently credit sales are converted into cash. According to a 2024 CPA Journal analysis, using an average instead of a single data point minimizes the effects of seasonal fluctuations, which are common in industries such as retail and construction.
For example, a company that starts the year with $40,000 in receivables and ends with $60,000 would have an average receivable of $50,000. This average becomes the denominator in the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio formula, producing a more accurate reflection of how frequently the company collects outstanding debts.
What Are Net Credit Sales and How Do They Impact AR Turnover?
Net Credit Sales are the total revenue generated from sales made on credit, minus any returns, allowances, or discounts granted to customers. The formula is:
Net Credit Sales = Total Credit Sales – Sales Returns – Allowances – Discounts
These sales directly impact the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio, as they represent the total receivables expected to be collected within the accounting period. A 2023 QuickBooks survey on financial management found that over 72% of small businesses use net credit sales data to evaluate their collection efficiency.
When net credit sales are high but the turnover ratio is low, it suggests that customers are taking longer to pay their invoices, potentially leading to cash flow challenges. In contrast, consistent net credit sales combined with a strong turnover ratio indicate that the business maintains healthy liquidity and effective credit management.
For instance, many companies, such as wholesalers and subscription-based software providers, rely heavily on credit transactions. Accurate tracking of net credit sales allows them to manage credit risks and forecast receivable inflows, ensuring operational stability.
What Is a Good Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio for Businesses?
A good Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio for businesses typically ranges between 7 and 10, depending on the industry. Yes, this range reflects efficient credit management and timely collections. According to a 2024 survey by the National Association of Accountants, companies with a turnover ratio above 8 often experience stronger cash flow and reduced bad debt risk.
The ideal ratio, however, varies across sectors. For example, retail and consumer goods companies may have higher ratios due to frequent customer payments, while construction or B2B service providers may record lower ratios because of longer credit terms. A business with a turnover ratio of 9, for instance, collects its receivables approximately every 40 days, which is considered excellent liquidity performance.
Experts from JMAccountingServices recommend evaluating turnover trends over time rather than relying on a single ratio. A consistently high or improving ratio signals effective collection procedures, while a declining one may indicate deteriorating payment behavior or relaxed credit policies.
What Does a High Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio Indicate?
Yes, a high Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio indicates that a business is collecting its receivables efficiently and converting credit sales into cash rapidly. This reflects strong credit control and effective collection processes. According to research published in the CPA Journal, companies with higher turnover ratios are better positioned to reinvest their cash into operations, reduce borrowing costs, and improve liquidity.
For example, businesses such as technology service firms and retail chains benefit from high turnover ratios because they rely on quick cash conversion to fund inventory and operational expenses. A ratio above 10 means that customers pay invoices on average every 36 days or less, suggesting prompt payment behavior and low default risk.
However, experts caution that an extremely high ratio could signal overly strict credit policies that might discourage potential clients. Therefore, balance is essential. The goal is to maintain a ratio that promotes liquidity while supporting sustainable customer relationships. Regular analysis through accounting professionals at JMAccountingServices can help businesses optimize their ratio and maintain financial stability.
What Causes a Low Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
A low Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio is caused by delayed collections, lenient credit policies, or inefficient billing processes that prevent timely cash inflows. According to the CPA Practice Advisor’s 2024 financial analysis, businesses with low ratios often struggle with extended payment cycles, leading to cash flow constraints and higher risk of bad debts.
Common causes include:
- Loose credit approval standards that allow high-risk customers to purchase on credit without adequate verification.
- Ineffective collection procedures, such as inconsistent follow-ups or lack of reminder systems.
- Disputes or billing errors that delay invoice reconciliation.
- Economic downturns, which can lead to slower customer payments.
For example, many small construction companies and consulting agencies face low turnover when clients delay payments for large projects. A consistent ratio below 5 may signal that the business is not converting receivables fast enough, potentially forcing it to rely on loans to sustain operations.
To correct this, experts recommend tightening credit terms, implementing automated invoicing tools, and conducting periodic credit reviews. Engaging accounting professionals through JMAccountingServices can help evaluate customer payment trends and improve collection efficiency.
How to Implement Accounts Receivable Turnover in Accounting?
Implementing the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio in accounting involves integrating it into routine financial reporting and performance analysis. Yes, this process helps businesses monitor liquidity and credit efficiency continuously.
The steps include:
- Collect accurate data on net credit sales and accounts receivable from the general ledger.
- Compute the ratio periodically, preferably quarterly or annually, to track changes in payment behavior.
- Compare results against industry benchmarks, as highlighted in CPA Journal studies, to identify whether the company is performing above or below standard.
- Integrate ratio findings into management decisions, such as adjusting credit policies, revising collection timelines, or identifying high-risk customers.
For example, a mid-sized e-commerce company might calculate its turnover each month to assess whether recent promotional credit offers are affecting cash flow. This continuous tracking provides early insights into liquidity challenges before they escalate. Accounting experts from JMAccountingServices recommend embedding this metric into management dashboards or financial KPIs to strengthen decision-making accuracy and forecasting reliability.
How Does Accounts Receivable Turnover Relate to Days Sales Outstanding?
The Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio directly relates to Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) as both measure how efficiently a company collects its receivables. Yes, DSO converts the turnover ratio into the average number of days it takes for a business to collect payments after a sale. The formula for DSO is:
Days Sales Outstanding = 365 ÷ Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
This relationship provides deeper insight into cash flow performance. For instance, a turnover ratio of 9 means the DSO is approximately 41 days, indicating that customers pay invoices within that timeframe. According to a 2024 QuickBooks research report, companies maintaining DSO under 45 days typically demonstrate strong financial discipline and stable liquidity.
While the turnover ratio measures collection frequency, DSO reflects the time duration between sales and payments. Many organizations, such as logistics firms and wholesalers, use both metrics together to monitor credit health and detect early signs of delayed payments.
Lower DSO values indicate faster collections and healthier cash cycles, while higher values suggest inefficiencies. Financial specialists from JMAccountingServices can assist businesses in analyzing both indicators to balance credit growth and cash availability effectively.
What Are the Limitations of Using Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
The limitations of using the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio arise from its dependency on averages and assumptions that may not fully represent real-time financial conditions. According to a 2024 Journal of Accountancy report, the ratio provides a snapshot rather than a complete picture of a company’s collection performance.
One key limitation is that it relies on historical data, which might not reflect current customer payment behaviors or economic conditions. For example, many manufacturing and seasonal businesses experience fluctuating sales cycles, yet the ratio averages these figures, potentially masking collection delays during slow periods.
Another limitation is that the ratio does not distinguish between high-value and low-value receivables. A single large overdue account can significantly distort results, even if smaller accounts are paid promptly. Moreover, the ratio assumes that all sales are on credit, which may not be true for mixed payment systems where cash sales form a portion of total revenue.
Additionally, changes in accounting policies or write-offs can alter the ratio without indicating real improvement or deterioration. Therefore, financial experts recommend analyzing the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio alongside other liquidity indicators—such as Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and Current Ratio—for a balanced view of financial efficiency.
How to Improve Your Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
To improve the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio, businesses must strengthen credit management and accelerate collections without straining customer relationships. Yes, effective implementation of credit control practices can significantly enhance liquidity and reduce bad debt exposure.
Practical strategies include:
- Tightening credit policies to ensure that customers undergo proper vetting before being granted credit terms.
- Issuing invoices promptly after delivery of goods or services to avoid unnecessary payment delays.
- Offering early payment discounts, such as 2/10 net 30, which incentivizes customers to pay sooner.
- Implementing automated reminders and collection systems to track overdue accounts efficiently.
- Regularly reviewing aging reports to identify and act on delinquent accounts before they become uncollectible.
For example, many companies, such as software subscription providers and wholesalers, use automated accounting software to send payment alerts and streamline follow-ups. According to a 2024 CPA Practice Advisor study, organizations that digitized their invoicing processes saw an average improvement of 22% in collection speed within six months.
Experts from JMAccountingServices recommend conducting periodic reviews of client credit limits and establishing consistent communication with customers to maintain a steady cash flow.
Where to Hire an Expert to Handle Accounts Receivable Turnover?
Skilled professionals to handle Accounts Receivable Turnover can be hired through JMAccountingServices, a trusted provider of accounting and financial management solutions. The firm specializes in helping businesses analyze financial ratios, implement data-driven collection strategies, and optimize cash flow performance.
At JMAccountingServices, clients can access certified accountants who are experienced in applying analytical tools and benchmarking performance against industry standards. Many companies, such as startups, retail enterprises, and consulting firms, rely on these experts to maintain accurate receivable tracking and ensure timely payments.
Engaging professional services ensures that calculations for turnover ratios, net credit sales, and Days Sales Outstanding are precise and aligned with current accounting standards. In addition, financial consultants can help identify underlying collection challenges, streamline reporting processes, and build automated dashboards for continuous monitoring.
Partnering with JMAccountingServices empowers businesses to strengthen their liquidity position, minimize receivable risks, and achieve consistent growth through improved financial efficiency.
